
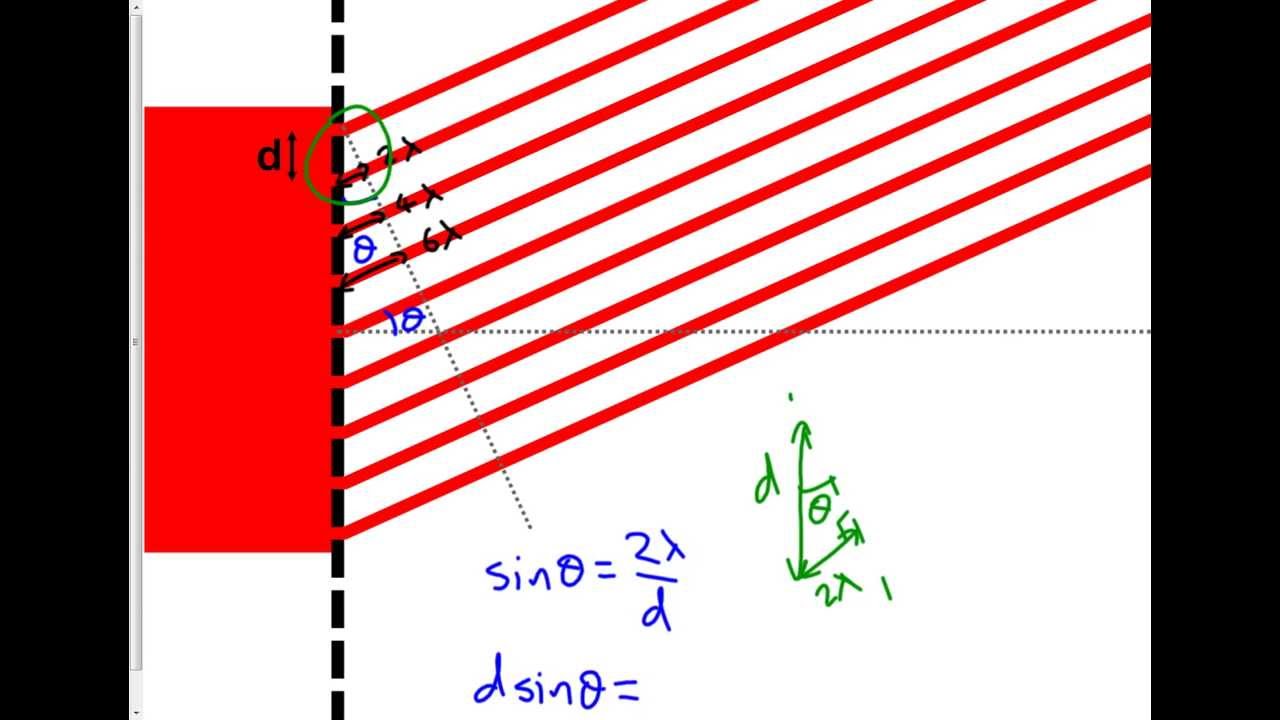

It means that most of the optical power is in the designed order, while minimum power is lost to other orders, especially in zero order. It is an explicit form of transmission or reflective diffraction grating, which is designed to yield maximum efficiency for a specific order. The incident is reflected by the rulings on the surface at different angles corresponding to different wavelengths and orders.įor both the transmission and reflective gratings, the zero-order mode shows no diffraction pattern, and the light either reflects or transmits.īlazed Gratings: It is also called echelette grating. These gratings can also be created by making plastic imprints of the original master copy. Reflective Gratings: Reflective gratings are formed by placing the metallic coating on parallel slits in the surface. Light can scatter through these parallel narrow slits. Transmission Gratings: Transmission gratings are formed by scratching the transparent fibre repeatedly, creating parallel lines. But, if the path difference is equal to λ, the waves are in phase and interfere constructively. At any point on the screen, if the path difference of light from the adjacent slits is equal to λ/2, the waves are out of phase and interfere destructively. The light diffracts through the grating and propagates in allĭirections. Consider a plane wave having wavelength λ of monochromatic light incident normally on each slit. m = 0), and no diffraction takes place at this point.įor diffraction to occur, the grating is made up of slits of spacing d, which are wider than the wavelength of interest. A grating also has a zero-order mode (i.e. Gratings may be of the reflective or transmissive type. Where d is the separation between the slits, λ \lambda λ is the wavelength of the incident light, D is the distance of screen from the incident beam, q is the phase difference, and y is the displacement from the centreline for maximum intensity. The above equation is known as the diffraction grating equation. The condition for maximum intensity is the same for single or double slit.ĭ sin θ = m λ d\sin \theta = m\lambda d sin θ = m λ Constructive interference occurs if the path length is an integral multiple of the wavelength of light. On the other hand, if crest falls on crest and trough falls on trough, it is called constructive interference, and the light at that point is brighter.Ī diffraction grating consists of a large number of closely packed parallel slits. If a trough falls on a crest, the waves cancel, and destructive interference occurs. These wavefronts undergo either constructive interference or destructive interference, depending on how the crests and troughs of the waves are related. According to Huygens’s Principle, each point on a wavefront behaves like a new source, which means that each slit acts as a new source. The rays and wavefronts form an orthogonal set such that the wave fronts are parallel to the grating and perpendicular to the rays. Consider a beam of parallel light rays falling on a grating.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
